👋 Hello Students!
Aaj hum Exponents (Powers) ke rules ko bohot detail mein samjhenge. Sirf formula ratna nahi hai, hum samjhenge ki ye rules kaise aur kyun kaam karte hain.
Jab hum bade numbers (jaise distance to stars) ya bohot chote numbers (jaise size of atom) ke saath kaam karte hain, toh Exponents humare best friend ban jate hain! 🚀
🎥 Video Explanation
🇮🇳 Hindi Explanation
🇬🇧 English Explanation
📊 Infographic Summary
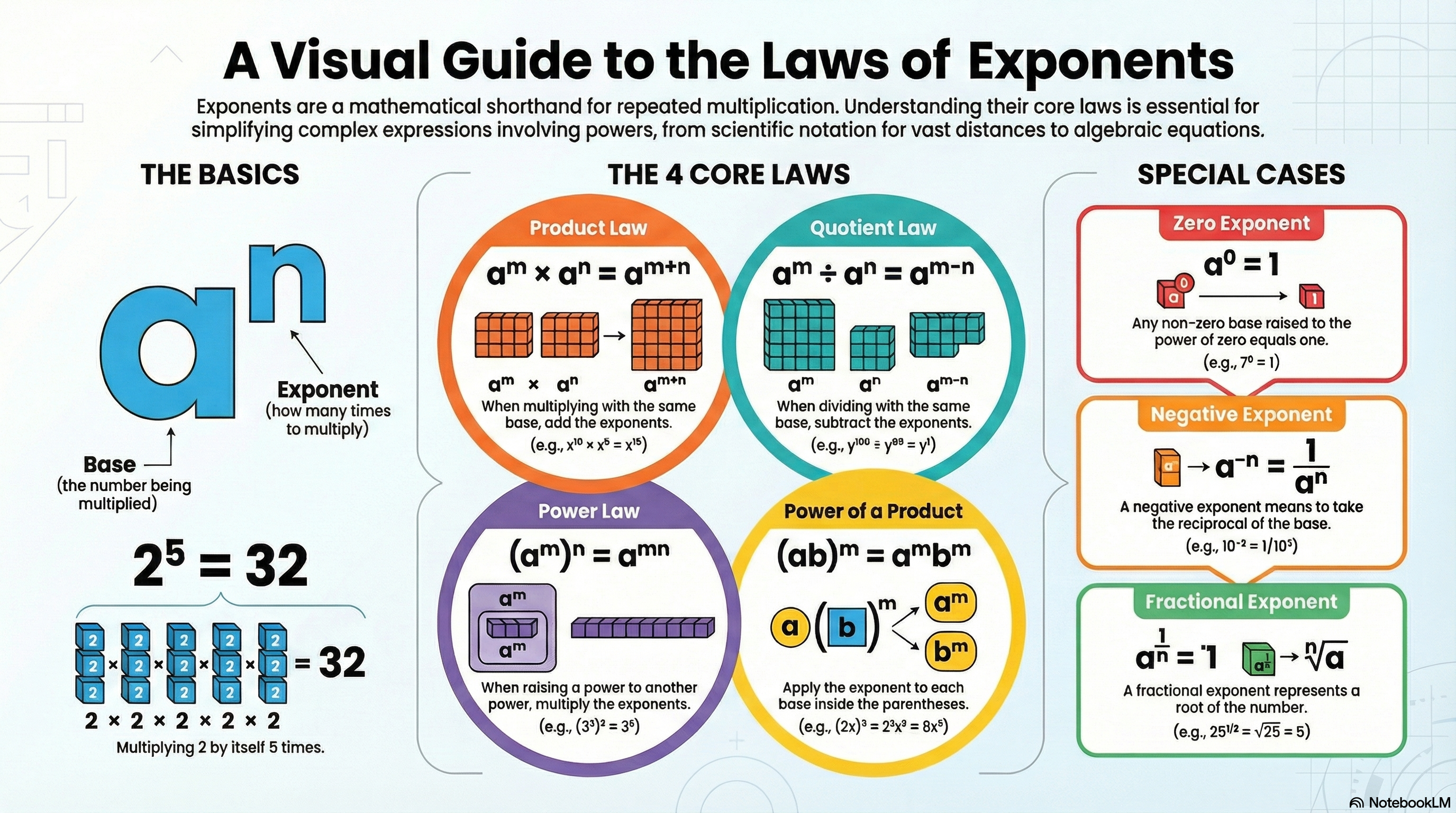
📜 Basic Concept: Base & Exponent
Base woh number hai jo "Hero" hai, aur Exponent uska "Power Level" hai. Jaise game mein power-up lene se hero strong ho jata hai, waise hi exponent batata hai ki base kitni baar multiply hokar strong banega. Agar 2⁵ hai, toh 2 hero hai aur 5 uska power level hai!
Expression: aⁿ
- Base (a): Woh number jo multiply ho raha hai.
- Exponent (n): Woh number jo batata hai ki base kitni baar multiply hoga.
2⁵ ka matlab hai:
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 (2 ko 5 baar multiply kiya)
Answer: 32
⚖️ The 4 Main Laws of Exponents
1. Product Law (Multiplication Rule)
Imagine karo do teams hain. Agar base same hai (matlab team same hai), toh hum bas unke players (powers) ko count karke add kar dete hain. Multiplication ka matlab hai powers ka milan (addition)!
Logic: Jab base same ho, toh hum bas powers ko count kar rahe hain.
Example: 2² × 2³ = (2×2) × (2×2×2) = 2⁵ (Total 5 baar 2 hai).
- Simple:
2³ × 2⁴ = 2³⁺⁴ = 2⁷ = 128 - With Negative Power:
5⁶ × 5⁻² = 5⁶⁺⁽⁻²⁾ = 5⁴ = 625 - With Variables:
x¹⁰ × x⁵ = x¹⁵
2. Quotient Law (Division Rule)
Division ek ladai (battle) ki tarah hai. Upar wali power aur neeche wali power ek dusre ko cancel karti hain. Jo power badi hoti hai, wahi jeetti hai (subtract karke bachi hui power).
Logic: Division mein upar wale numbers neeche wale numbers se cancel ho jate hain. Jo
bachta hai wo difference hota hai.
Example: 2⁵ ÷ 2² = (2×2×2×2×2) / (2×2) = 2×2×2 = 2³.
- Simple:
10⁸ ÷ 10⁵ = 10⁸⁻⁵ = 10³ = 1000 - Result Negative:
2³ ÷ 2⁵ = 2³⁻⁵ = 2⁻²(Iska matlab 1/2² hai) - With Variables:
y¹⁰⁰ ÷ y⁹⁹ = y¹⁰⁰⁻⁹⁹ = y¹ = y
3. Power Law (Power of Power)
Ye "Power ke upar Power" hai! Jaise ek building ke upar dusri building khadi kar di ho. Is case mein hum powers ko multiply kar dete hain taaki total height pata chale.
Logic: Iska matlab hai groups of groups.
Example: (2²)³ ka matlab hai 2² ko 3 baar likho:
2² × 2² × 2² = 2²⁺²⁺² = 2⁶. (Short trick: 2 × 3 = 6).
- Simple:
(3²)³ = 3²ˣ³ = 3⁶ = 729 - With Fraction:
(2³)² = 2⁶ = 64 - Complex:
(x⁻²)³ = x⁻⁶
4. Different Base, Same Power
Agar do alag-alag log (bases) same umbrella (power) ke neeche aa jayein, toh woh ek saath chal sakte hain. Pehle unhe multiply karo, phir umbrella lagao!
Logic: Agar power same hai, toh hum bases ko pehle multiply kar sakte hain, phir power laga sakte hain.
- Simple:
2³ × 5³ = (2 × 5)³ = 10³ = 1000(Easy calculation!) - Variables:
x⁵ × y⁵ = (xy)⁵ - Division Case:
10⁴ / 5⁴ = (10/5)⁴ = 2⁴ = 16
👻 Special Cases: Zero & Negative Powers
The Zero Exponent Rule
Ye maths ka "Magic Spell" hai. Koi bhi number ho, kitna bhi bada kyu na ho (except 0), agar uske sir par 0 baith gaya, toh wo turant 1 ban jata hai!
a⁰ = 1 (Where a ≠ 0)
Logic: Pattern dekho:
2³ = 8
2² = 4 (Divide by 2)
2¹ = 2 (Divide by 2)
2⁰ = 1 (Divide by 2 again!)
7⁰ = 1(12345)⁰ = 1(x + y)⁰ = 1
The Negative Exponent Rule
Negative sign ek "Lift" ki tarah hai. Agar power negative hai, toh wo number ko neeche (denominator mein) le jati hai aur positive ban jati hai. Agar neeche negative hai, toh upar le aati hai.
a⁻ⁿ = 1 / aⁿ
Logic: Negative sign ka matlab hai "Divide" ya "Reciprocal". Ye multiplication ka ulta hai.
2⁻¹ = 1/2(Half)10⁻² = 1/10² = 1/100 = 0.01(3/4)⁻¹ = 4/3(Fraction palat gaya!)
🧩 Fractional Exponents (Roots)
Fraction power ka matlab hai "Root". Agar power 1/2 hai, toh wo Square Root hai. Agar 1/3 hai, toh Cube Root. Ye number ko chota karne ka tareeka hai.
Fraction power ka seedha connection Roots se hai.
a¹/ⁿ = ⁿ√a
aᵐ/ⁿ = (ⁿ√a)ᵐ
25¹/² = √25 = 5
49¹/² = √49 = 7
27¹/³ = ∛27 = 3 (Kyunki 3×3×3 = 27)
125¹/³ = 5
Find 4³/²
Trick: Pehle root nikalo, phir power lagao.
Step 1: 4¹/² = 2 (Square root of 4)
Step 2: 2³ = 8 (Cube of 2)
Answer: 8
📝 Practice Questions
Solve these to check your understanding:
- Simplify:
(25)³/² - Evaluate:
(64/125)⁻²/³ - Simplify:
7¹/² × 7³/²
Show Answers
1. 125
(√25 = 5, then 5³ = 125)
2. 25/16
(Flip fraction: 125/64. Cube root: 5/4. Square:
25/16)
3. 49
(Powers add: 1/2 + 3/2 = 4/2 = 2. So 7² = 49)